Presentation of the exercise
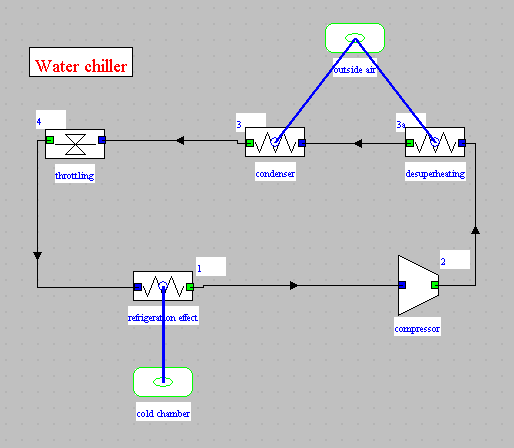
This exercise is primarily intended to illustrate how to model in Thermoptim a refrigeration cycle. It deals with the study of a 100 kilowatts water chiller, used to keep food at a temperature of a few degrees Celsius.
This exercise is divided into several parts:
- Initially, the chiller diagram is built
- It is then transferred in the simulator and set
- The cycle is then plotted in the entropy chart, and qualitatively compared with the reverse Carnot cycle
- Finally, we show how to estimate the impact of a change of fluid on the thermodynamic performance of the chiller, the R12 being replaced by R134a
Exercice groupe frigorifique
- 100 kW water chiller
- fluid: R12
- evaporation pressure: 3 bar
- condensation pressure: 10 bar
- Refrigerant flow-rate: 0.836 kg/s
- compression isentropic efficiency: 0.75
- superheating: 5 °C
- subcooling: 5 °C
Opening of Thermoptim
- two screens at opening
-
diagram editor
-
simulator
Thermoptim
Thermoptim
Thermoptim
Thermoptim
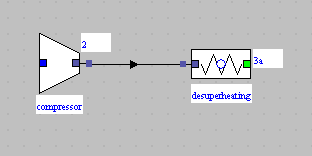
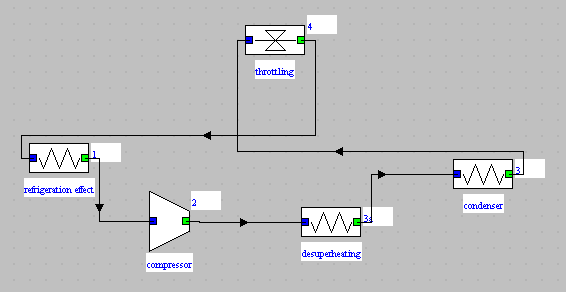
- diagram of the chiller
- compressor
- desuperheater, condenser
- throttling
- refrigeration effect
Thermoptim
Thermoptim
- diagram simulator interface
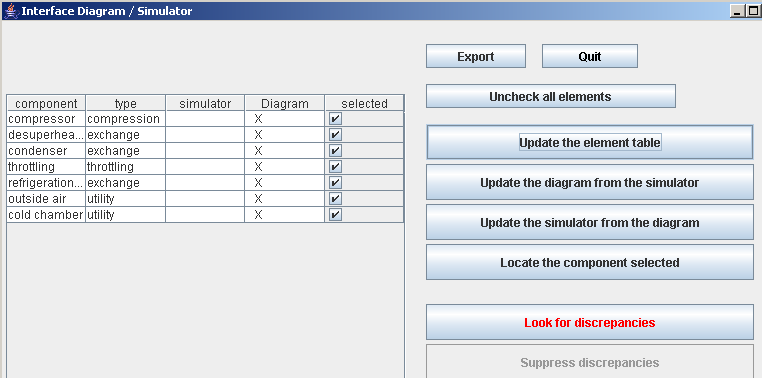
Thermoptim
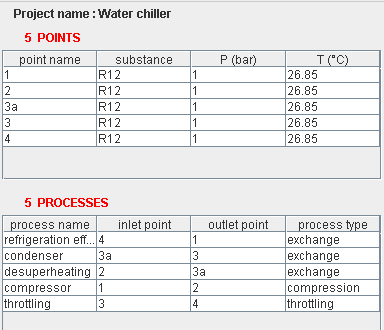
Setting model parameters
When the elements of the simulator are created, Thermoptim initializes all the points with a pressure of 1 bar and a temperature of 300 K, which must then be modified according to the nature of the problem you are studying.
The two activities that follow will show you how to set points and transformers, then the next you remember the values you enter that in Thermoptim.
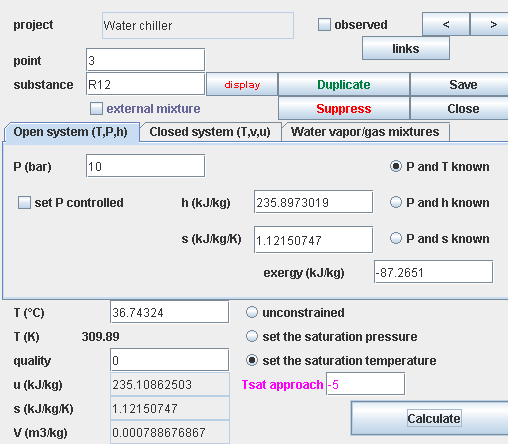
Point settings
- double-click on a link (arrow) on a line of the point table
- thermodynamic state of a small volume of matter
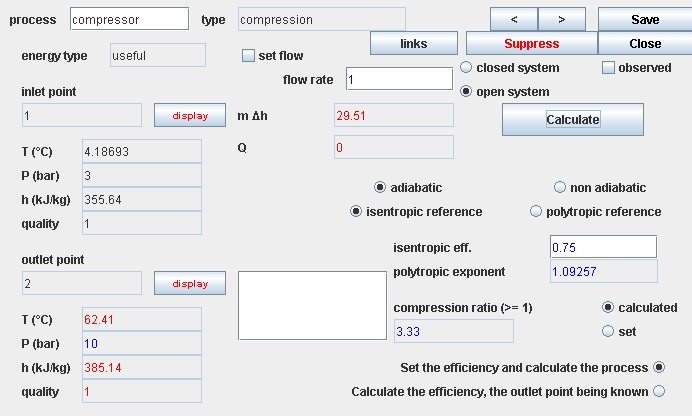
Setting processes
- double-click on a component or on a process table line
- fluid mass flow-rate
Setting the parameters of points and processes
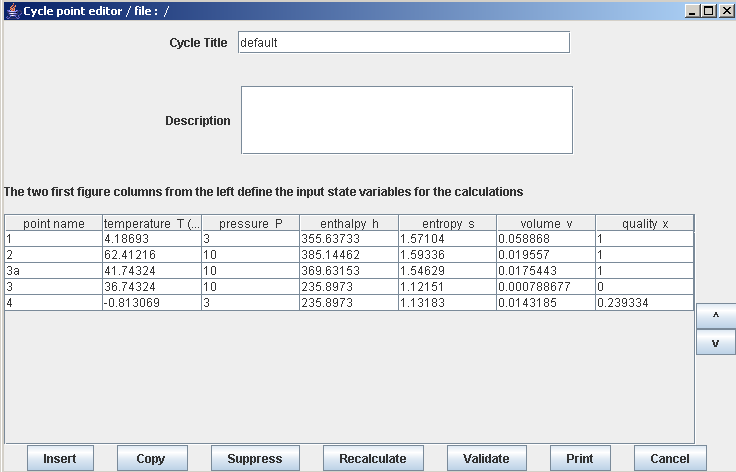
Set now the parameters of the various points one by one, checking that you enter the values of the temperatures known, as well as those of the pressures, as Thermoptim does not set them automatically. In order to do that, follow these steps:
- open point 1 (R12 in the vapor state), enter a pressure 3 bar and choose “set the saturation temperature”, set the quality to 1 and a Tsat approach equal to 5 °C, then click on “Calculate” which sets the temperature to about 4.2 °C.
- then open point 2, enter a pressure of 10 bar, and click on “Calculate”
- open point 3a, enter a pressure 10 bar and choose “set the saturation temperature”, set the quality to 1, then click on “Calculate” which sets the temperature to about 41.7 °C
- open point 3, in the same conditions, its quality being set to 0 and Tsat approach to - 5 °C, then click on “Calculate”
- open point 4, enter a pressure of 3 bar, and click on “Calculate”
Set then the process’s parameters, for which default options are valid:
open process “compressor”, and enter an isentropic efficiency of 0.75, then click on “Calculate”, which sets the temperature of point 2 (62.4 °C)
open processes “desuperheating”, and “condenser”, and click on “Calculate”. The temperatures of their inlet and outlet points being known, their enthalpies can be calculated
open process “throttling”, which has no particular setting, then click “Calculate”, which determines point 4 saturation temperature (-0.81 ° C) and a quality of 0.24
open process “refrigeration effect”, can be calculated, points 4 and 1 being known
The calculation of the overall balance requires to understand the notion of energy type, explained in the next activity.
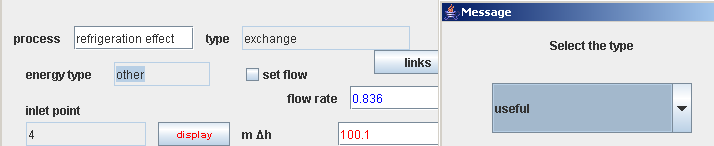
Energy type choice in processes
- double-click on the energy type field
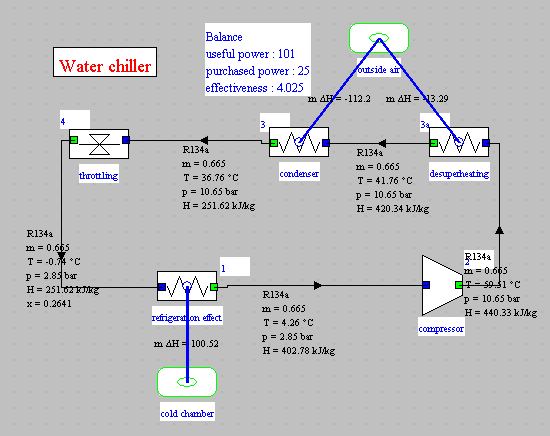
Balance and synoptic view
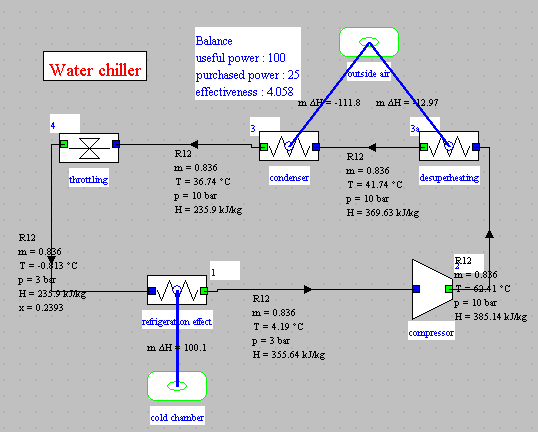
- R12
- -1 °C
- 41 °C
- 3 / 10 bar
- η = 0.75
- COP = 4
Cycle on (T,s) chart
- interface diagrammes-simulateur
Cycle on (T,s) chart
Cycle on (T,s) chart
Cycle on (T,s) chart
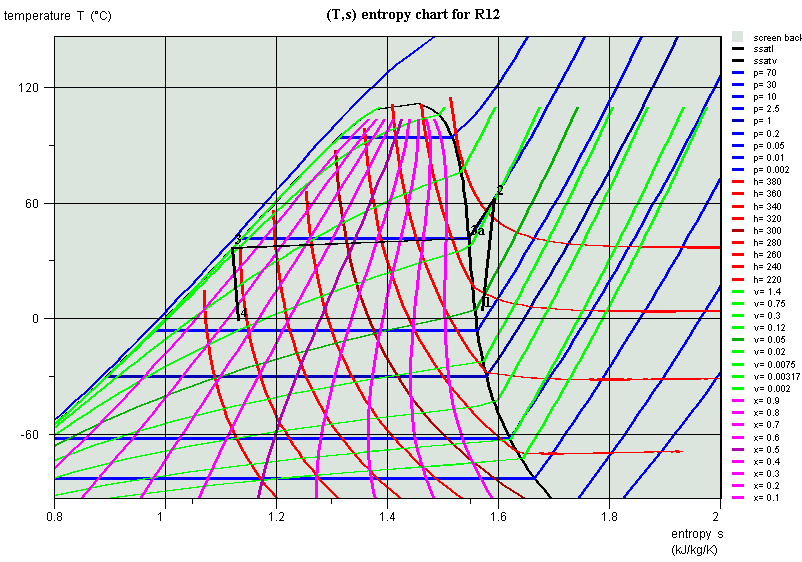
Cycle on (T,s) chart
Cycle on (T,s) chart
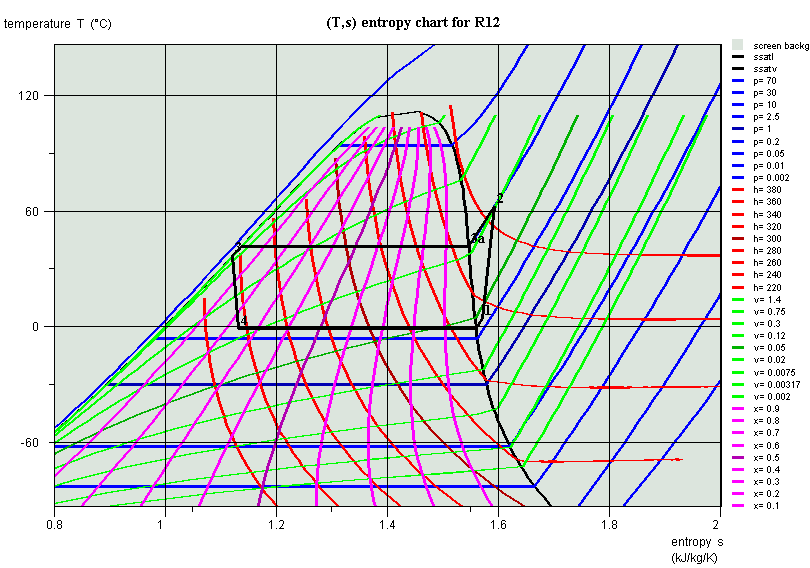
Cycle on (h,P) chart
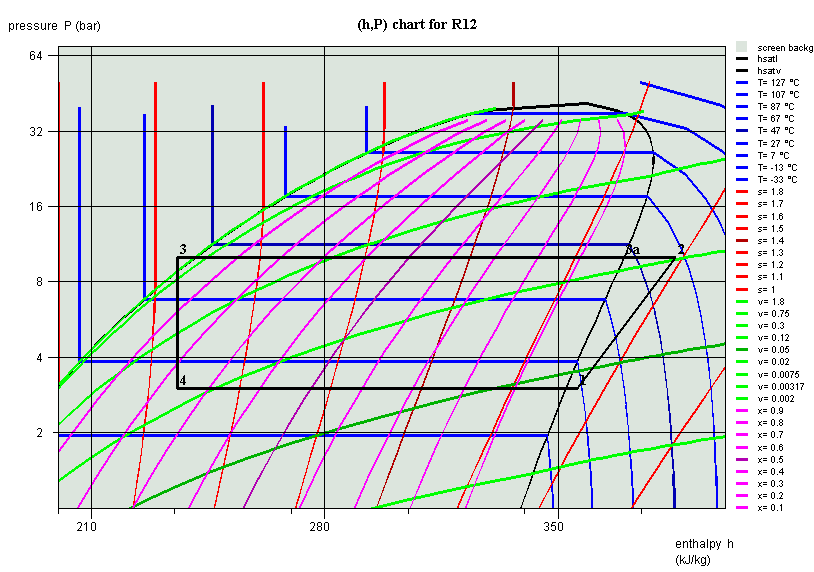
Comparison with Carnot cycle
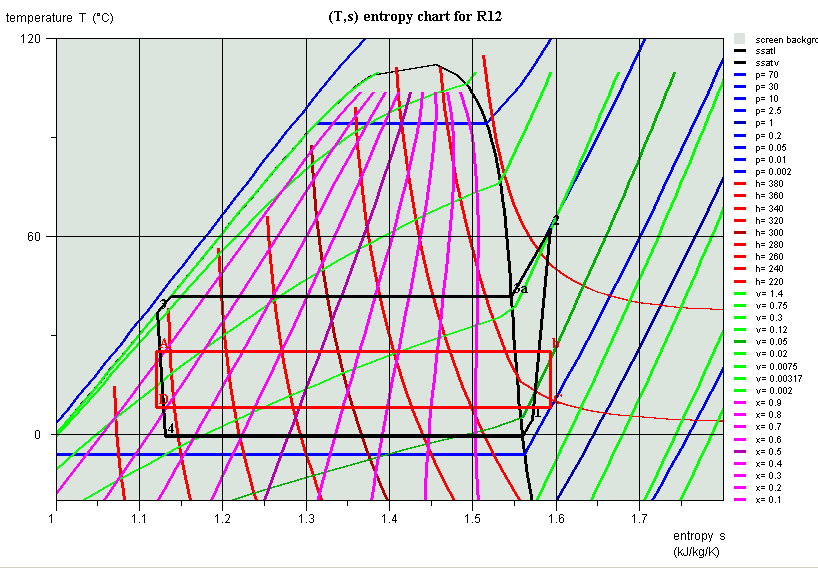
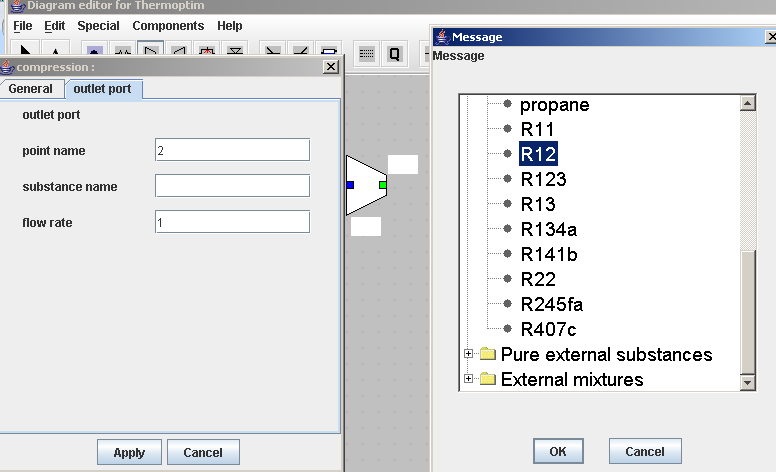
Change of refrigerant
The model you have built has allowed you to accurately determine the performance of the water chiller studied. We have considered fluid R12 as refrigerant, but its use was banned since 1994 by the Montreal Protocol. In the following steps, you will see how easily you can change a substance in Thermoptim.
The solution files of this exercise are included in the archive that you can download from a link at the bottom of this page.
The interest to model cycles with a software package is that the properties of substances are calculated with great precision and without any difficulty. Once the model is developed, you can quite easily change its settings, allowing you to rapidly make sensitivity studies on the influence of various parameters.
This working manner involves however a risk: that you do not criticize the values provided by the software package, which can lead you to grant a disproportionate confidence to the results it provides.
It can happen that the model is not well built, and that its results are not right, and it is necessary to know to diagnose this type of errors. To do this, you should be able to check by yourself its results, at least in an approximate way.
It is in particular recommended to check the energy balances well. In order to do that, train to recompute them roughly, by summing on a bit of paper all the useful energies like all purchased energies, and by dividing them to obtain the cycle efficiency.
You will find below a link towards a note entitled “Model construction and verification methodology” intended to provide Thermoptim users with a certain number of recommendations based on past experience.
Thermoptim
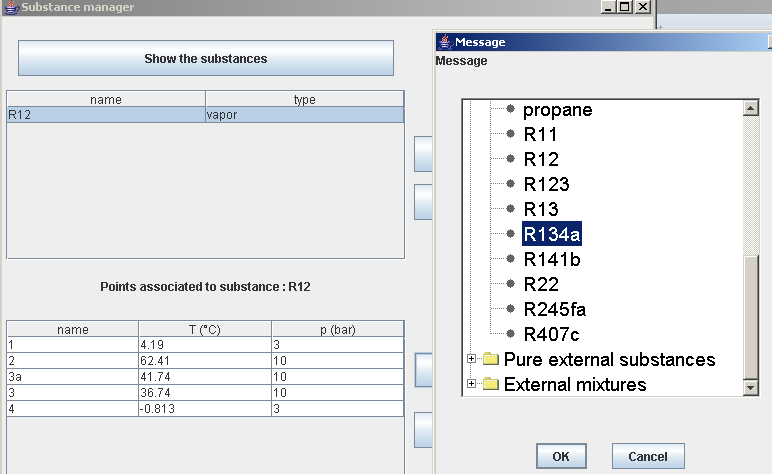
Balance and synoptic view
- R134a
- -1°C
- 41°C
- 2,85/10,65 bar
- η = 0.75
- COP = 4